To create a new Environment, select Environment from the sidebar menu. Then click, +Add Application and complete the information in the pop-up window. Click Add.
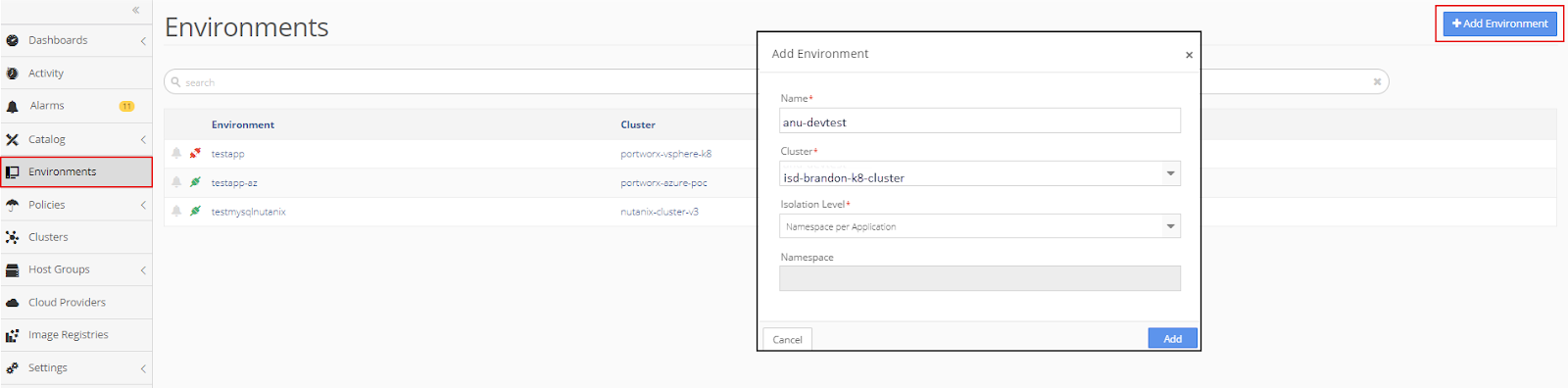
The new environment appears in the Environments menu.
In this example, a new mysql application is created and run in the new environment.
To create a new mysql Application, add the mysql YAML to the Application Catalog.
mysql YAML:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: wordpress-mysql
labels:
app: wordpress
spec:
ports:
- port: 3306
selector:
app: wordpress
tier: mysql
clusterIP: None
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: mysql-pv-claim
labels:
app: wordpress
spec:
storageClassName: rook-ceph-block
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 20Gi
---
apiVersion: apps/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: wordpress-mysql
labels:
app: wordpress
spec:
strategy:
type: Recreate
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: wordpress
tier: mysql
spec:
containers:
- image: mysql:5.6
name: mysql
env:
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
value: changeme
ports:
- containerPort: 3306
name: mysql
volumeMounts:
- name: mysql-persistent-storage
mountPath: /var/lib/rook
volumes:
- name: mysql-persistent-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: mysql-pv-claim
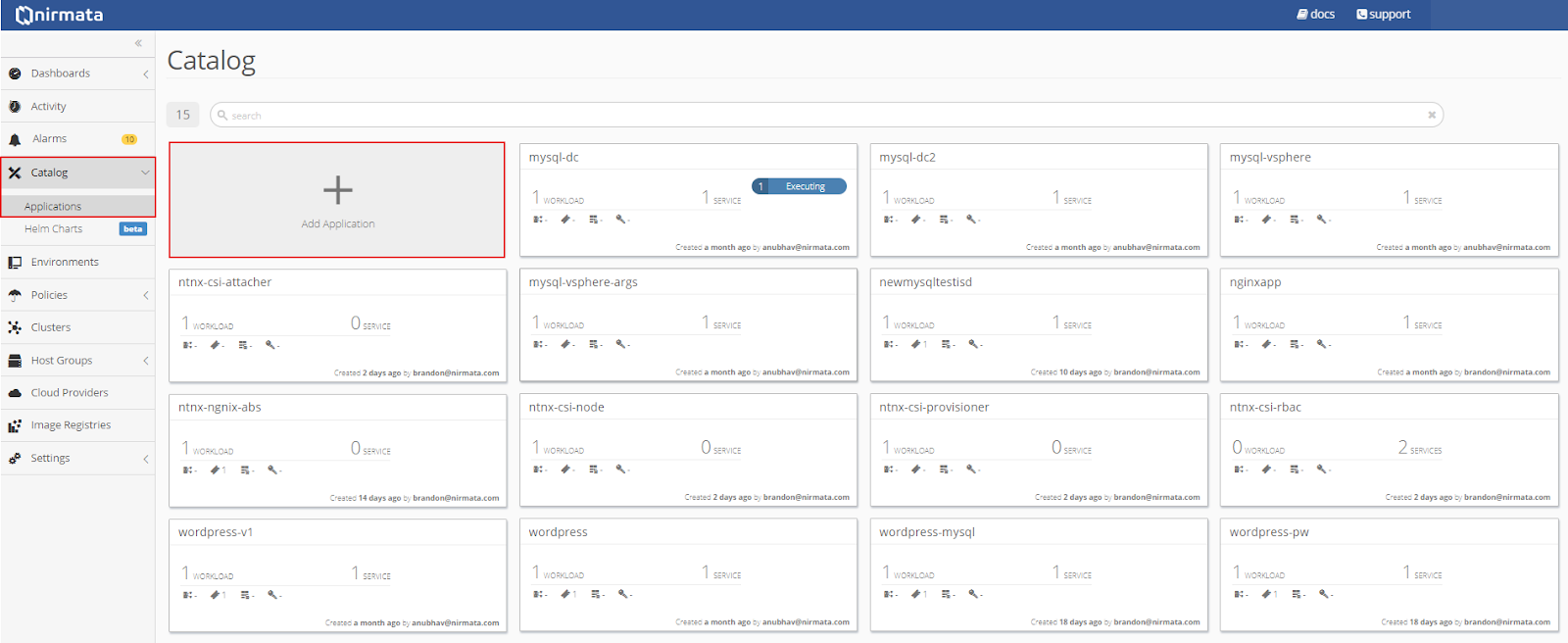
To add the mysql YAML to the Application Catalog, click on Catalog in the sidebar menu and then select Application Catalog. From the main Application Catalog screen, click Add Application.
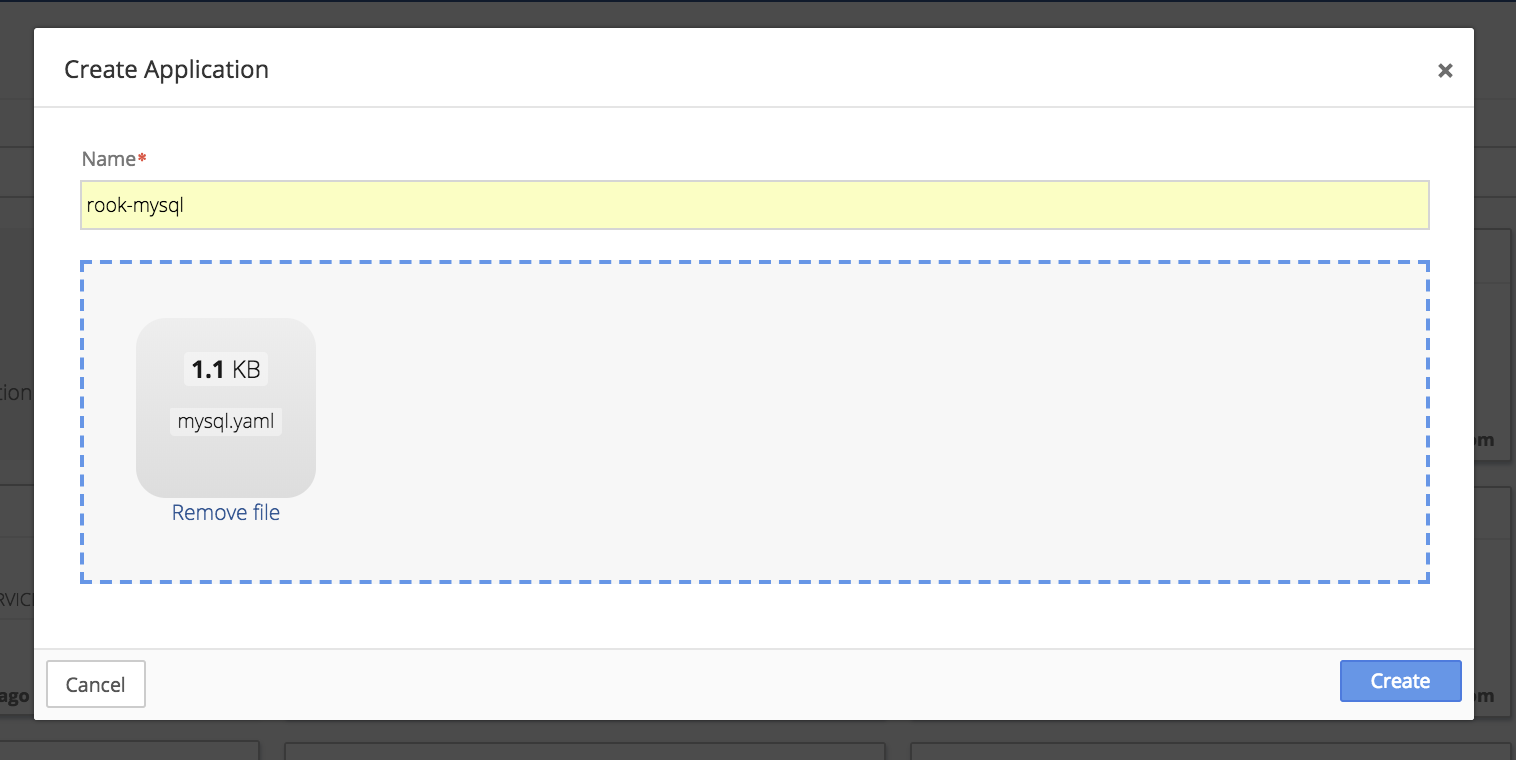
Drop the mysql YAML file into the upload box or select the file from the directory.
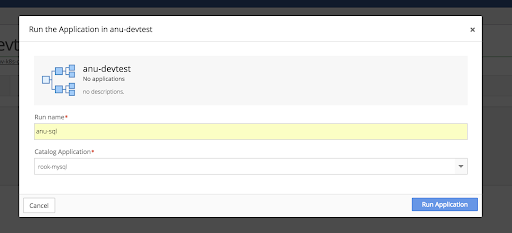
Run the mysql Application in the new Environment.
In the Environments menu, open the Environment that was just created. Click the gear in the top right corner of the Environments window and select the + Run an Application option.
Choose the mysql Application and click Run Application.
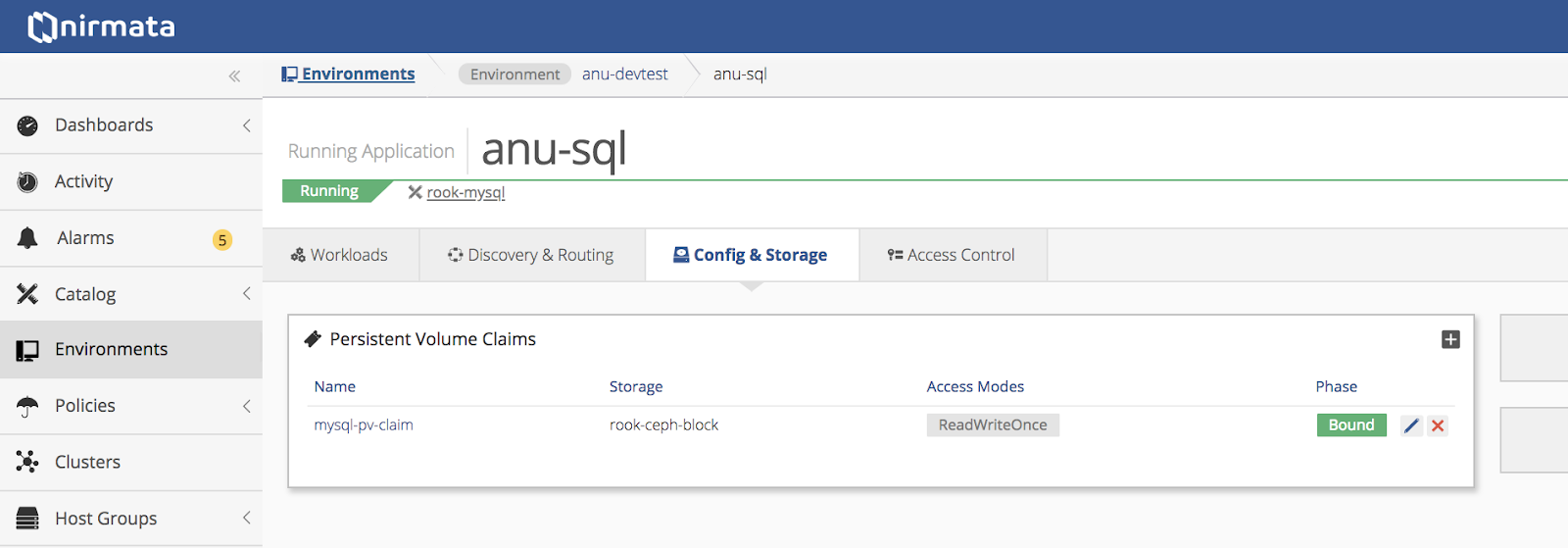
Verify that the Application is running using persistent volumes.
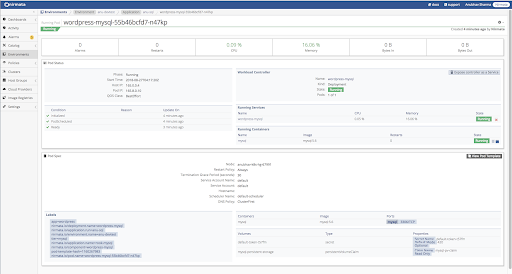
Verify workload status.
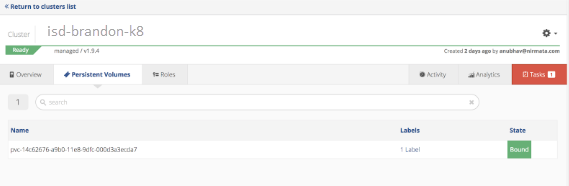
Verify persistent volume information.
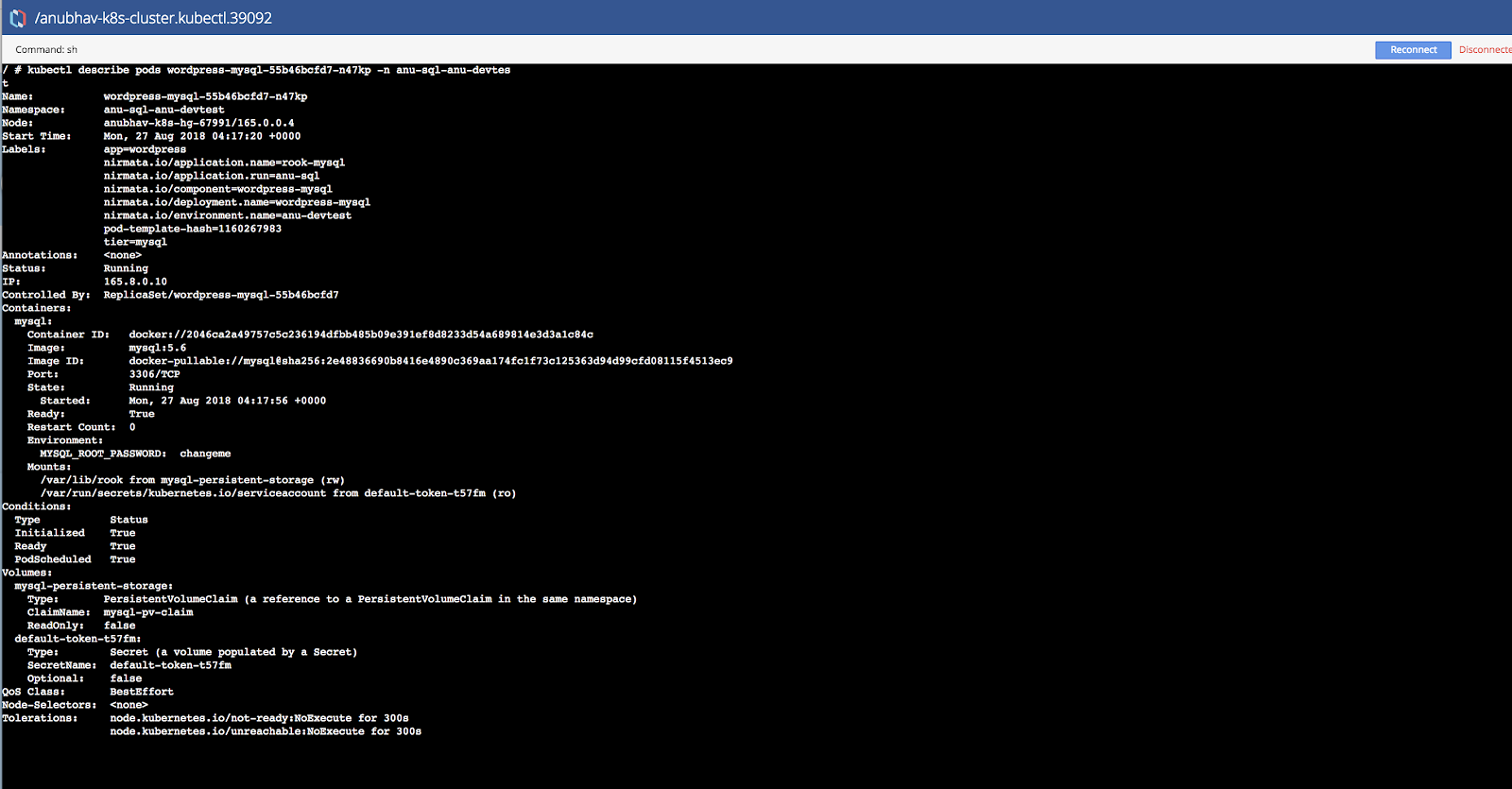
Verify pod status from Nirmata shell.