Resource Quota & Limit Range Overview
In Kubernetes, Resource Quota provides constraints that limit aggregate resource consumption per namespace. It can limit the quantity of objects that can be created in a namespace by type, as well as the total amount of resources that may be consumed by resources in that namespace.
If a resource quota is configured, then it is required that every incoming pod/container makes an explicit request for the required resources. If a resource request is not configured, the pod creation request is rejected. A Limit Range can be used to force defaults for pods that don’t specify resource requirements.
Support of Resource Quota and Limit Range within Nirmata allows users to allocate the resources of a cluster to specific teams or applications.
Resource Quota and Limit Range enables cluster resources, including CPU, memory, PVCs, and a variety of other quantities, to be divided between multiple teams or applications.
Nirmata checks the quantities used at the specified level. If the quantity is found to be above the specified threshold for more than three minutes, an alarm is raised in Nirmata.
Admin or platform user can specify the Default Resource Quota for an environment. This will be applied to any application/namespace that does not specify one.
-
Admin or platform user will be able to define a Default Limit Range for an environment. It will be applied to any application that does not specifying one.
-
Admin or platform user will be able to define an Environment Resource Quota.
-
An Alarm will be generated when the Resource Usage aggregated across all Applications exceeds the Environment Resource Quota
-
Admin or platform users can create/import/export/update/delete Resource Quotas and Limit Ranges in Environment configured with an “environment” level isolation.
-
Admin or platform users can create/import/update/view usage/delete Resource Quotas and Limit Ranges for applications deployed in Environments configured with an “application” level isolation.
-
All users can view the Resource usage for all the running applications in a given environment
-
All users will can view pod scheduling failure events related to Resource Quota and Limit Ranges
Resource Quotas set at the Environment level are not hard limits and will not prevent applications from running. Instead, when running an application exceeds the Resource Quota limits, an alarm is raised.
How to Set a Limit Range
Limit Range can be added to most Kubernetes resources but most often it is added to Container, Pod, PersistentVolumeClaim. Default values are required in the limit range for environments that use resource quotas so that any container that does not specify resource requests/limits can use the defaults.
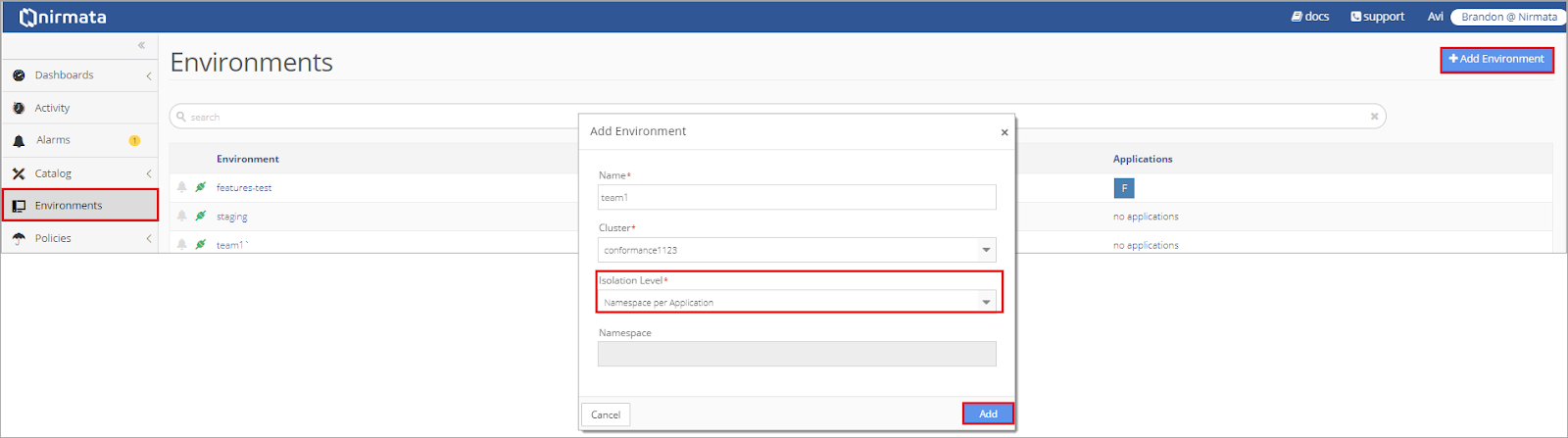
To apply a new Limit Range, create an Environment in Nirmata by selecting Environments and then the +Add Environment button. Complete the Add Environment wizard.
| Isolation Level Definitions | |
|---|---|
| Shared NameSpace | All applications deployed in the environment are in the same namespace; each application can only be deployed one time |
| Namespace per Application | Each application can be deployed multiple times; deployment occurs within the application’s own Environment |
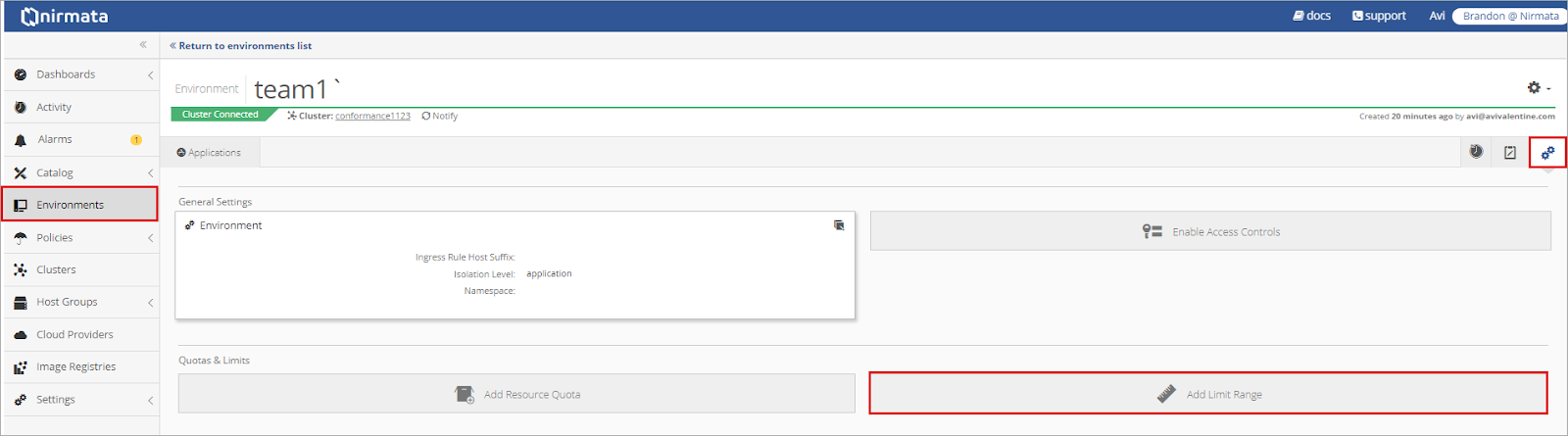
After creating the Environment, open the Environment settings and select Add Limit Range.
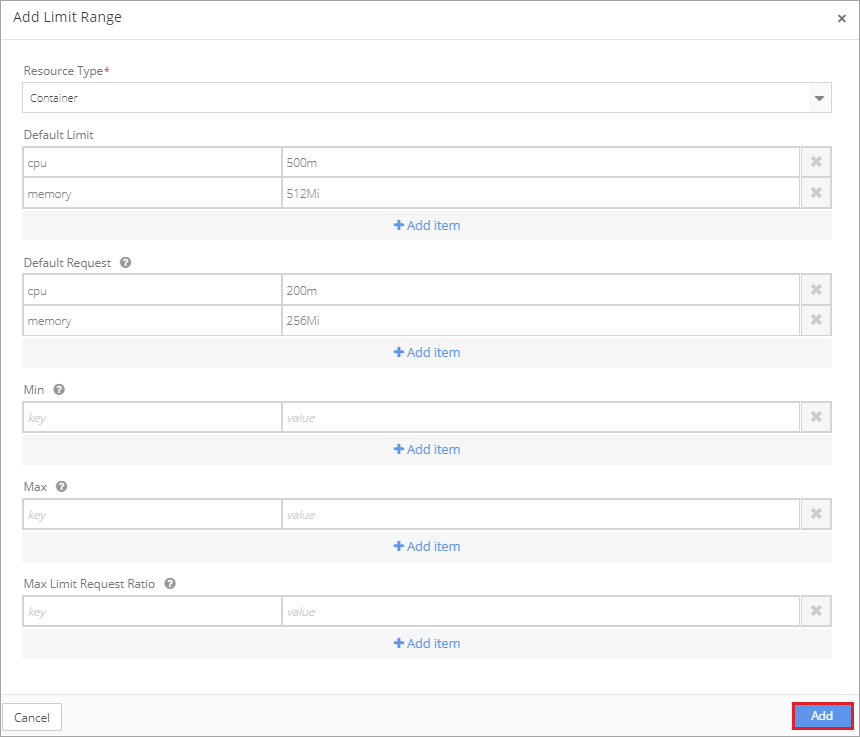
Specify the appropriate Default Limits to be applied at the container level. Each Default Level is the quantity that the container is guaranteed to have at start-up.
Default Request values are the quantities applied to containers that do not specify a request quantity. A Default Request is the minimum value for the specified resource and is applied to containers deployed in the environment.
Click the Add button after completing each Limit Range quantity.
How to Set a Resource Quota at the Environment Level
After setting a Limit Range at the container level, Resource Quotas can be defined at the Application Level and the Environment Level.
To add a Resource Quota, select Add Resource Quota from within the Environment Settings. Kubernetes compares current application usage levels to the defined Resource Quotas.
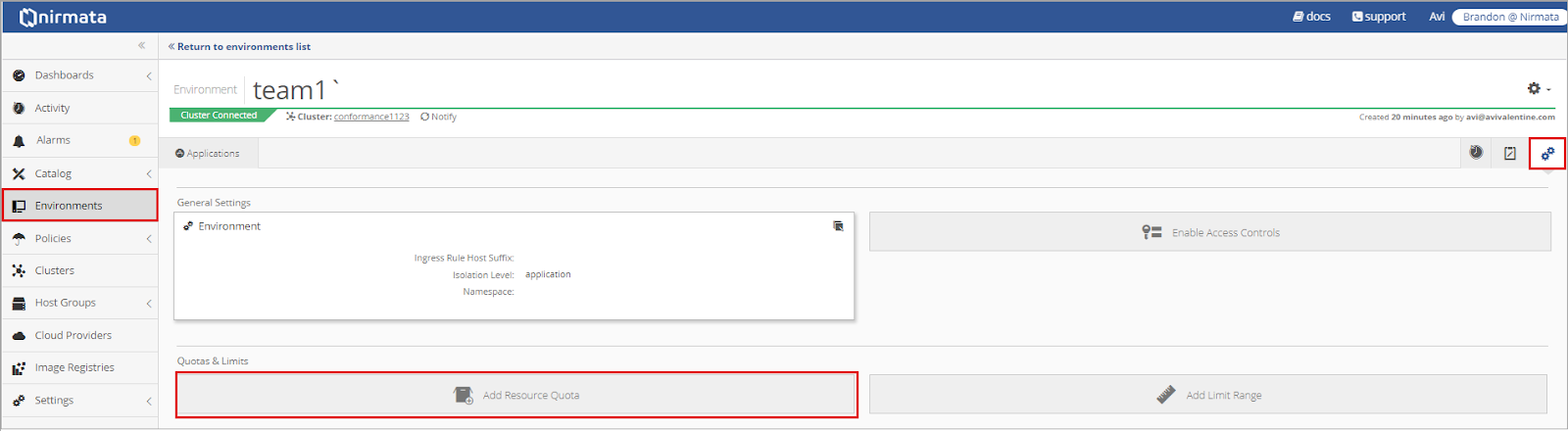
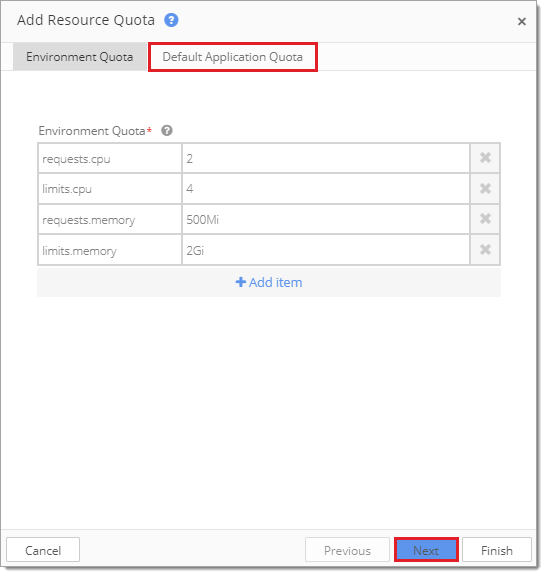
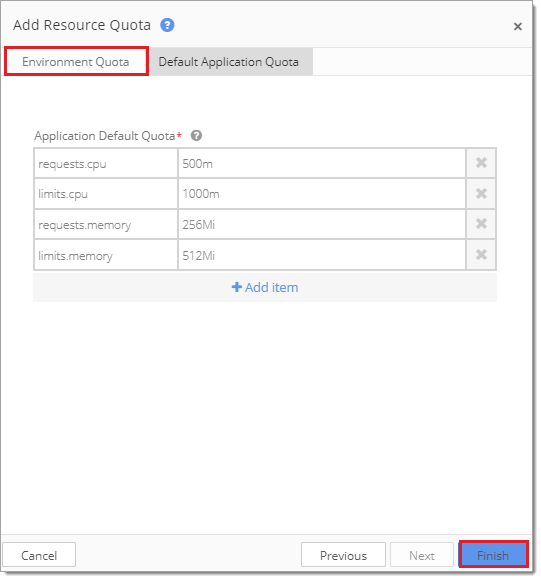
How to Set a Resource Quota at the Application Level
To set a Resource Quota at the Application level, select the Application from the Catalog and then click on the Deployment.
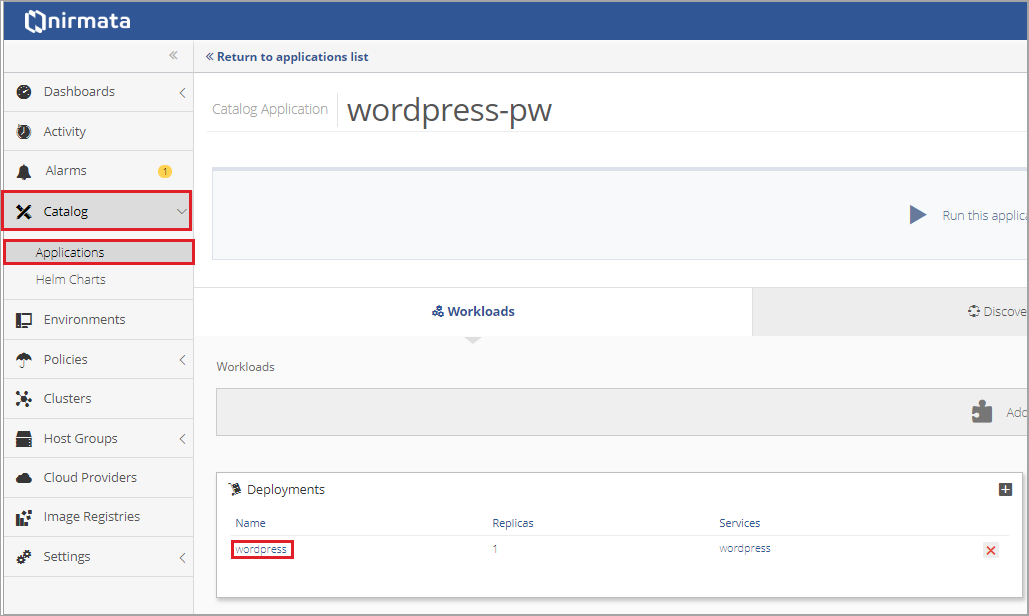
Select the Containers to which the Resource Quota will apply.
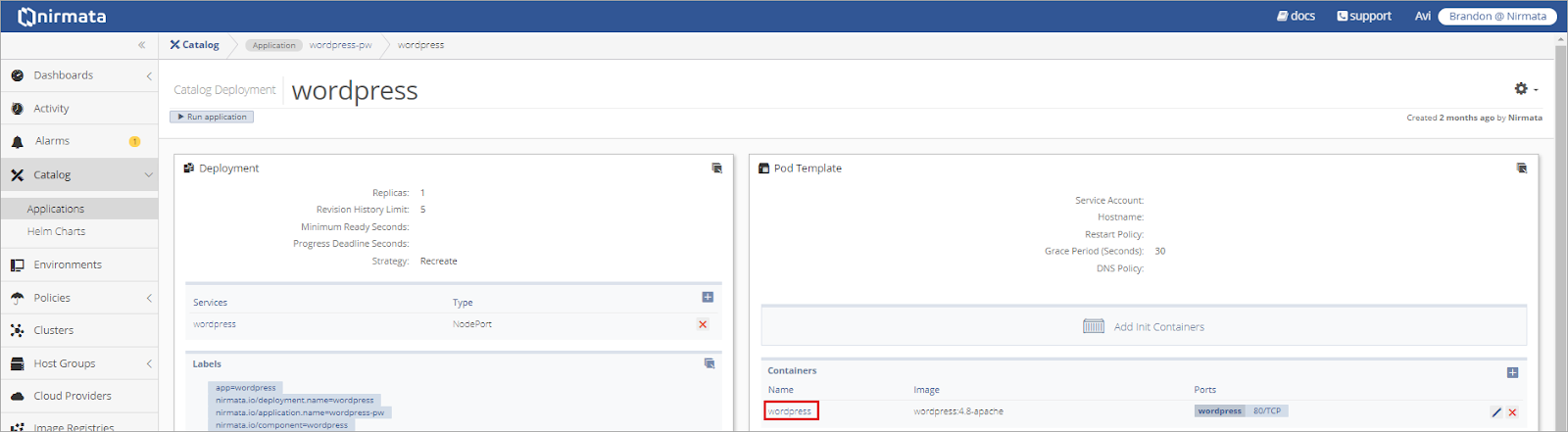
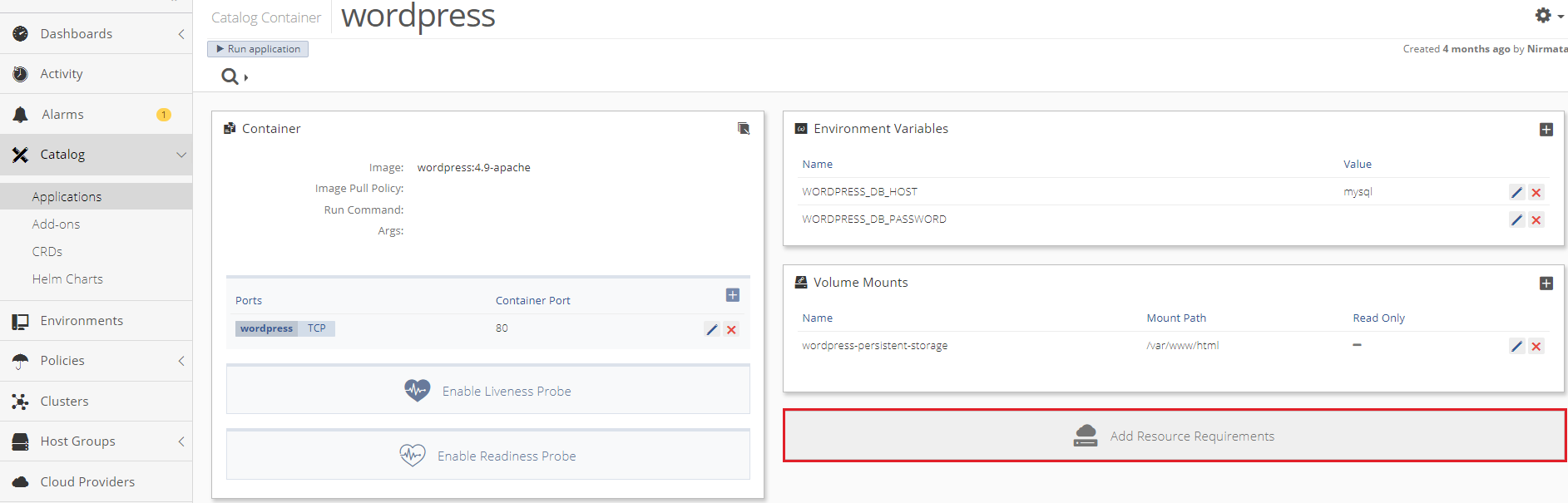
Click Add Resource Requirements.
Understanding Resource Quota Errors
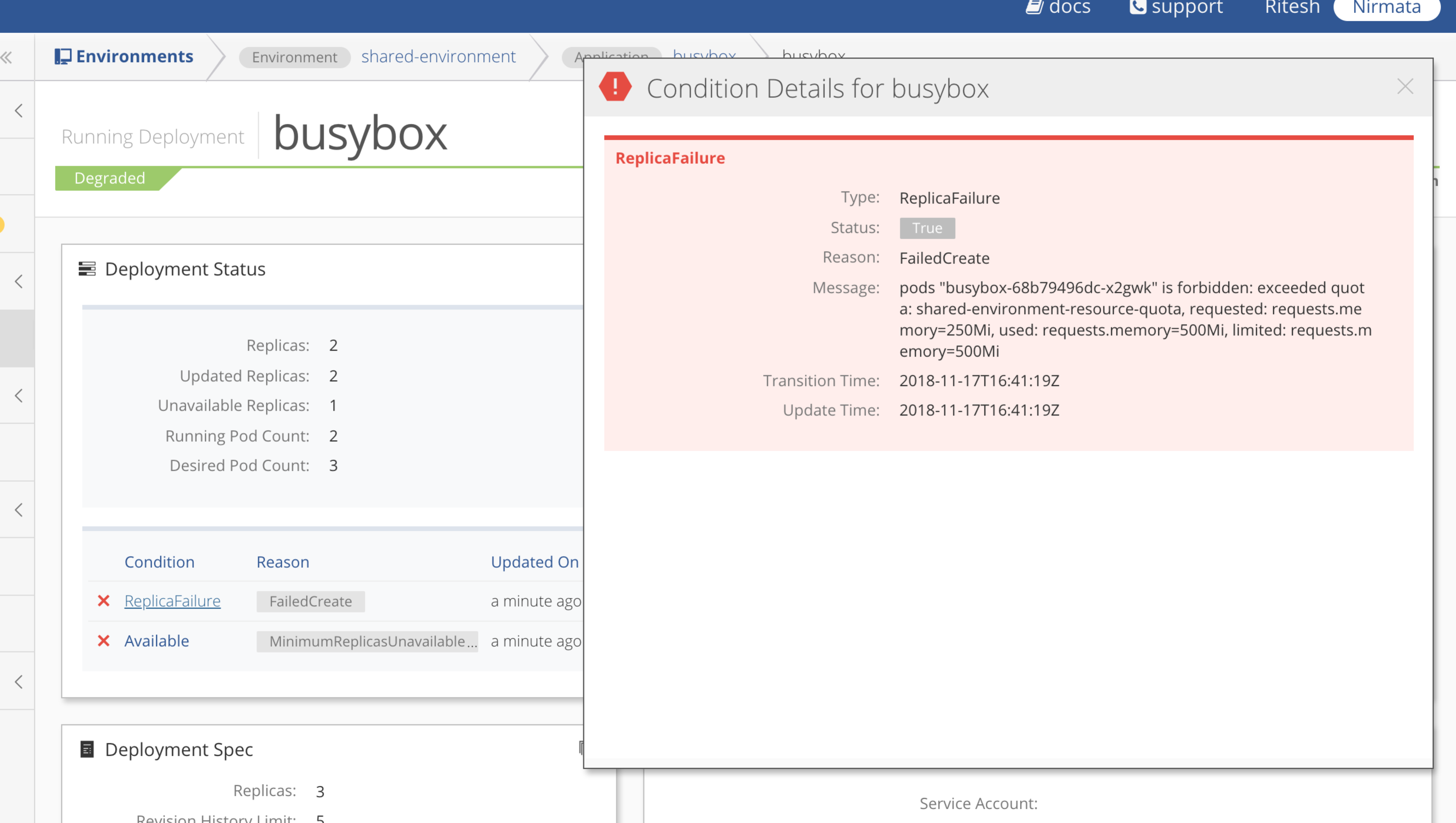
If the pod deployment fails when the resource quota is exceeded, the error details are displayed in Status.
For example, in a deployment, ReplicaFailure will display. View the details by clicking on the condition.
Understanding Resource Quota Alarms
Nirmata generates the following alarms when resource quotas exceed the configured thresholds:
-
Resource Quota CPU Usage: This alarm is triggered when the allocated CPU request is greater than the threshold.
-
Resource Quota Limits CPU Usage: This alarm is triggered when the allocated CPU limit is greater than the threshold.
-
Resource Quota Limits Memory Usage: This alarm is triggered when the allocated memory limit is greater than the threshold.
-
Resource Quota Memory Usage: This alarm is triggered when the allocated memory request is greater than the threshold.
Compute Resource Quotas
| Compute Resource Quotas | |
|---|---|
| cpu | Across all pods in a non-terminal state, the sum of CPU requests cannot exceed this value. |
| limits.cpu | Across all pods in a non-terminal state, the sum of CPU limits cannot exceed this value. |
| limits.memory | Across all pods in a non-terminal state, the sum of memory limits cannot exceed this value. |
| memory | Across all pods in a non-terminal state, the sum of memory requests cannot exceed this value. |
| requests.cpu | Across all pods in a non-terminal state, the sum of CPU requests cannot exceed this value. |
| requests.memory | Across all pods in a non-terminal state, the sum of memory requests cannot exceed this value. |
Storage Resource Quotas
| Storage Resource Quotas | |
|---|---|
| requests.storage | Across all persistent volume claims, the sum of storage requests cannot exceed this value. |
| persistentvolumeclaims | The total number of persistent volume claims that can exist in the namespace. |
| Across all persistent volume claims associated with the storage-class-name, the sum of storage requests cannot exceed this value. | |
| Across all pods in a non-terminal state, the sum of memory requests cannot exceed this value. |
Object Count Quota
Resource Quota can be added for any namespaced resource using the syntax:
count/<resource>.<group>
Following resources are supported:
| Supported Resources | |
|---|---|
| configmaps | The total number of config maps that can exist in the namespace. |
| pods | The total number of pods in a non-terminal state that can exist in the namespace. A pod is in a terminal state if is in Failed, Succeeded phase. |
| persistentvolumeclaims | The total number of persistent volume claims that can exist in the namespace. |
| replicationcontrollers | The total number of replication controllers that can exist in the namespace. |
| resourcequotas | The total number of resource quotas that can exist in a namespace. |
| services | The total number of services that can exist in the namespace. |
| services.loadbalancers | The total number of services of type load balancer that can exist in the namespace. |
| services.nodeports | The total number of services of type node port that can exist in the namespace. |
| secrets | The total number of secrets that can exist in the namespace. |